AraC is composed of 292 amino acid residues and uses the active sites formed by the amino acids
198-219 and 246-269 to bind to DNA. The isolated AraC protein binds to araO1(-100 to -144),
acting as an inhibitor. When the C protein binds with the inducer
AraBAD, forming a complex, it binds to the araI region (-40 to -78) allowing RNA Pol to bind to
the PBAD site (+140) and transcribe downstream genes.
TetR monomer is made up of 198 amino acid residues and, when dimerized, is folded by 10
alpha-helices connected by turns and loops. The three-dimensional structure of the TetR monomer
is mainly stabilized by hydrophobic inverse helices. The sequence of
amino acids 33-52 located at the N-terminal is the DNA binding region, composed of helices a1,
a2, a3, and their symmetric helices a1', a2', a3'. The regulatory core, composed of helices a5,
a10 and their symmetric helices a5',
a10', controls dimerization and the binding sites of each monomer in the presence of divalent
cations. Helices a5, a8, a10, and their corresponding helices form the core scaffold, and their
structure is the most conserved in the
entire TetR conformation.
To avoid significant protein structural changes, we only subjected the DNA binding sites of AraC
and TetR to computer-simulated random mutations. The optimized proteins obtained showed a slight
change in their DNA binding site structures through structural
simulations, while the rest of the structures remained largely unchanged. (Figure 6, Figure 7).
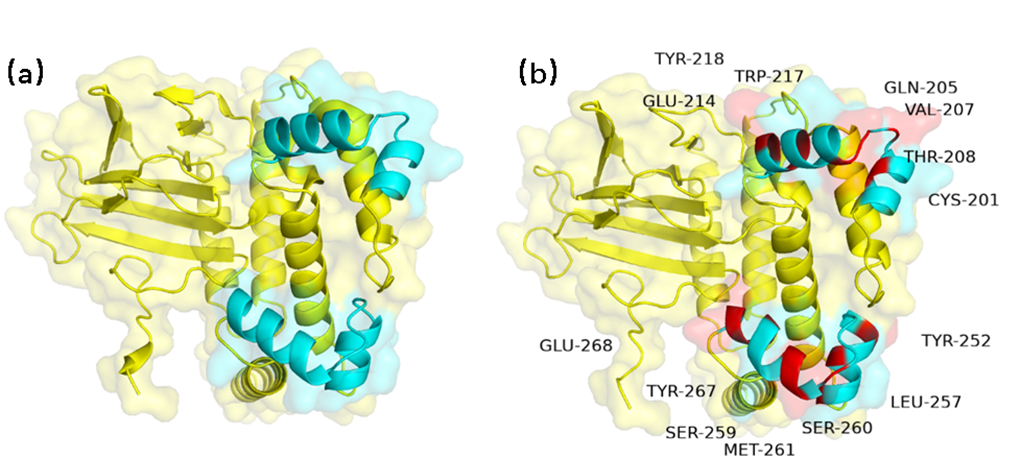
Comparison of AraC homologous modeling results. (a) Pre-mutation AraC structure (b) Homologous
modeling structure of post-mutation AraC. AraC rated P from 12.98 to 15.94 . The blue part is
the DNA-binding site of the protein, the yellow part is the rest
of the structure, and the red part represents the amino acid after the mutation.
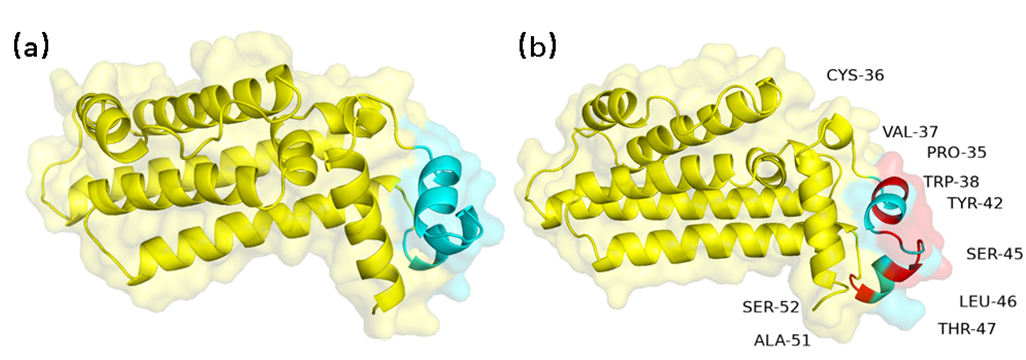
Comparison of TerR homologous modeling results. (a) Pre-mutation TetR structure (b)
Post-mutation TetR homologous modeling structure. The score P of TetR ranges from 5.38 to 8.19.
The blue part is the DNA-binding site of the protein, the yellow part is
the rest of the structure, and the red part represents the amino acid after the mutation.