April
Initial thoughts are established, and preliminary experimental design is underway.
Suitable target genes will be selected, along with appropriate chassis organisms and types of transformation plasmids.
May
Synthesize the gene and construct recombinant plasmids.
June
Prepare competent cells. Cultivate bacterial cultures and extract plasmids, followed by the transformation of the target gene into the chassis organism, Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (ECN1917). Synthesize DLPC-encapsulated engineered bacteria.
July
Verification of the functions of GLP-1 and BCoAT genes includes the following steps: Protein concentration in the supernatant will be measured using the BCA protein assay kit. For the determination of secreted proteins, the supernatant will be filtered through a 0.22 µm membrane. The expression of secreted proteins will be quantified according to the instructions of the GLP-1 ELISA kit. For Western blot analysis, log-phase bacterial cultures will be collected and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5 minutes. The supernatant will be collected and precipitated for colony counting. Using anti-His and anti-Flag antibodies, Western blotting will be performed to detect the negative control group, positive control group, the transformed internal reference gene protein BCoAT, and the expression of recombinant GLP-1 protein.
August
Assess bacterial viability using the CCK-8 assay and the DMAO/PI staining method for evaluating bacterial activity and cell death.
September
Utilize transmission electron microscopy to observe DLPC-encapsulated engineered bacteria.
Others
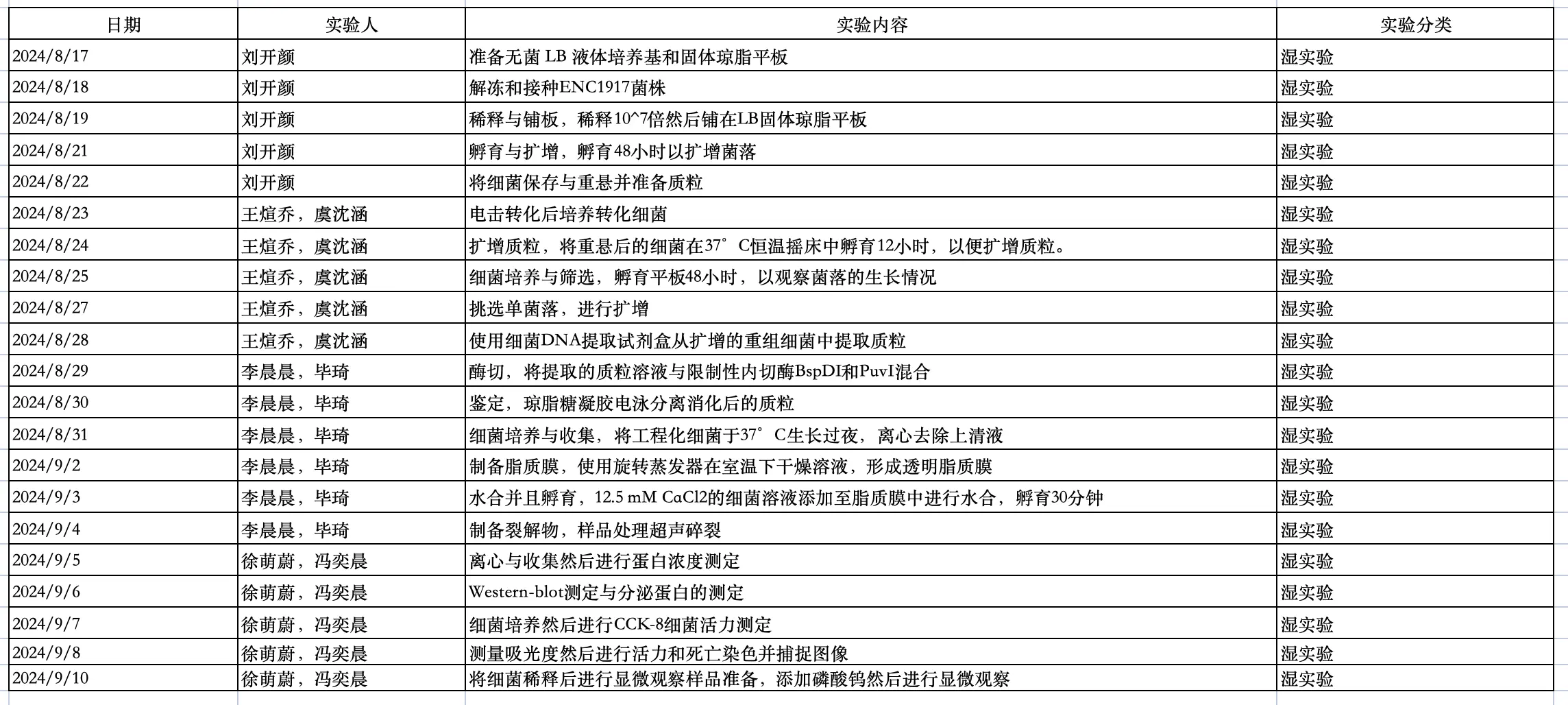
Our division of labor schedule.