In order to obtain mutants with better properties, we built protein models and calculated their mutable sites. By scoring the mutated models, we determined which ones were the best mutants. By calculating the energy of the molecules at docking, we can also verify whether the mutants are more active when reacting with the substrate.
| # | Site | Original residues | Mutational residues |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18 | Lys | Arg or Gln |
| 2 | 20 | Gln | Arg |
| 3 | 51 | Gln | Ala |
| 4 | 159 | Val | Phe or Leu |
| # | Site | Original residues | Mutational residues |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16 | Ser | Gly or Asp |
| 2 | 161 | Thr | Phe or Leu |
| 3 | 172 | Gln | Ile |
Table 1 and 2 show the point mutation sites provided by Hotspot Wizard. In the search for point mutations, reference was made to the original analysis of residue 291. All conserved residues in enzymes are composed of polar, nonpolar, acidic and basic groups. Most of the conserved residues, such as Tyr, Asn, Gly, Thr, Gln and Cys, belong to polar groups, followed by non-polar groups (Phe, Trp, Ala, Val and Pro), acidic groups (Glu and Asp) and basic groups (Arg and His). So we evaluated some functional residues as well as other residues.
Rosseta's Relax module was used to score these point mutation models. The initial model energy was calculated as -607.691. The energy of p.(K18R) was -332.407 and the structure was disorganized(Figure 1a), so the mutation scheme has been abandoned. The possible reason was that site 18 was mutated into Arg, and the surrounding area was positively charged, while Arg was negatively charged in the past, and the energy was too high, so the structure appeared to fall apart.
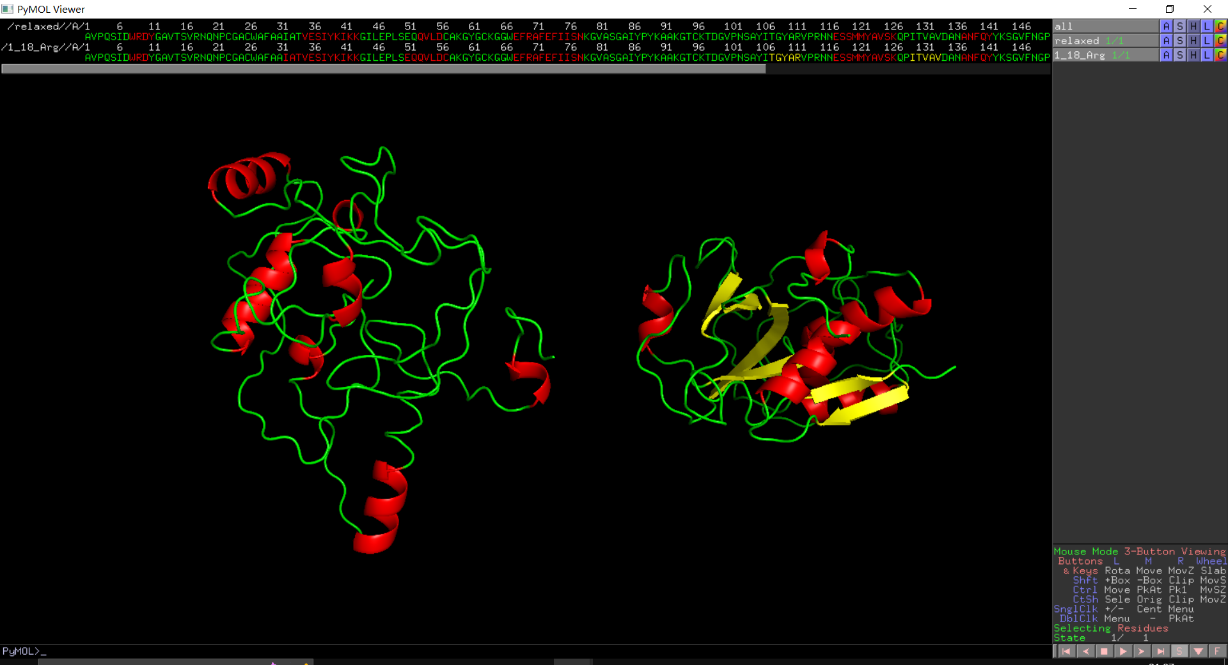
The energy of the p.(K18G)was -605.077. Although its structure did not fall apart, its energy increased and thus it was abandoned. The structure of p.(Q20R) was disintegrated after mutation, so it was abandoned too. (Figure 1b)
However, the energy of p.(S16G) was -610.561 after mutation. Meanwhile, compared with the structure before mutation, its RMSD value was 0.683, so it was selected for further mutation.(Figure 1 c)
Finally, we screened the model with Leu mutation at site 67, and its energy was -614.826. Compared with the original model, the RMSD value was 0.97. Its reduced energy and relatively stable structure suggested that it might be a better variant of bromelain, as the experiments would prove.
The definition of upper relationship means that some single mutations of A are unfavorable, but the addition of B mutation will have better performance than single B mutation, which means that B has upper relationship with A. After calculating by Relax, we found that the Gly single mutation at site 16 had an upper relationship with the Leu single mutation at site 67: when Leu single mutation was detected, the structure was disordered, RM value was 1.4, and energy was -348. But with the addition of Gly, the structure stabilizes and the energy drops to -614.82. At the same time, the single mutation of Gly at site 16 has an upper relationship with the single mutation of Val at site 64: the energy of single mutation of Val is -599, while the energy of mutation of both Gly and Val decreases to -608.
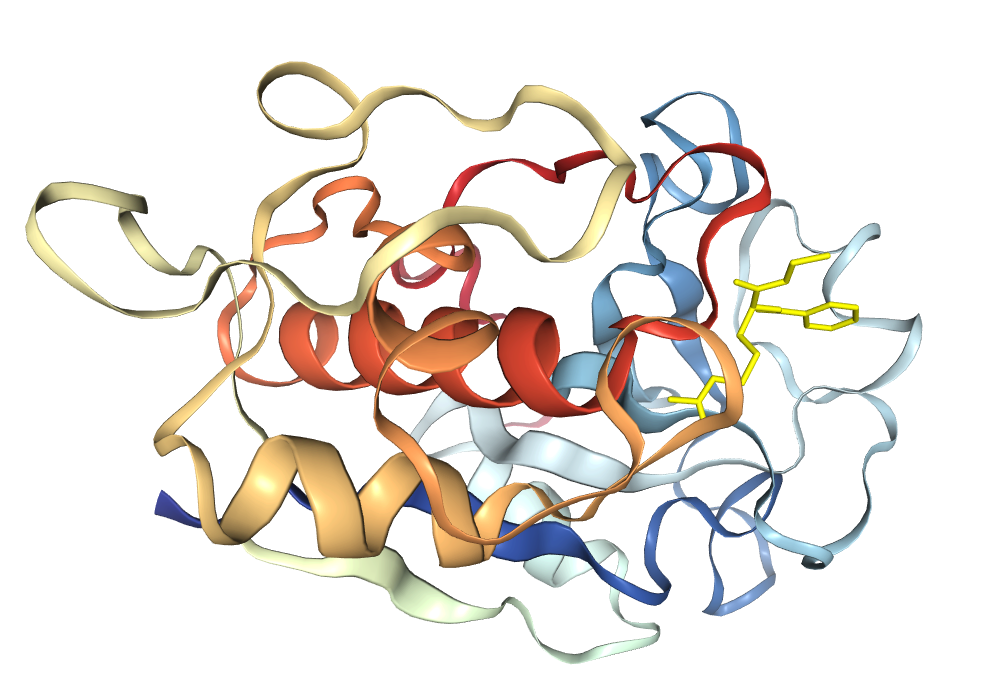
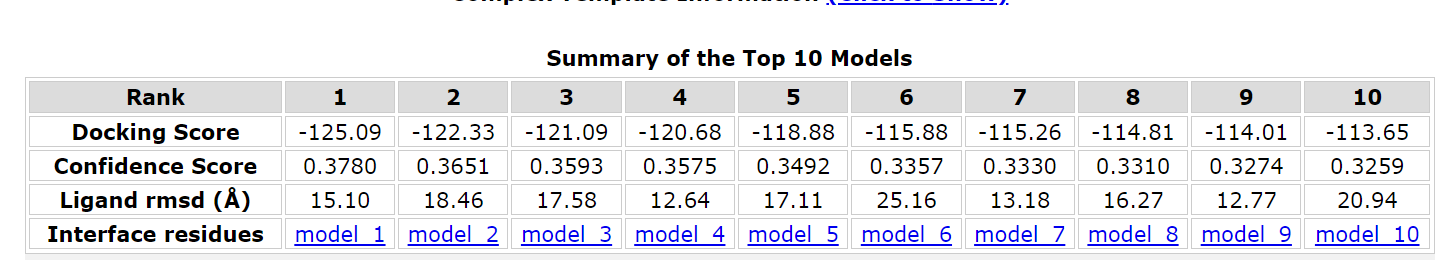
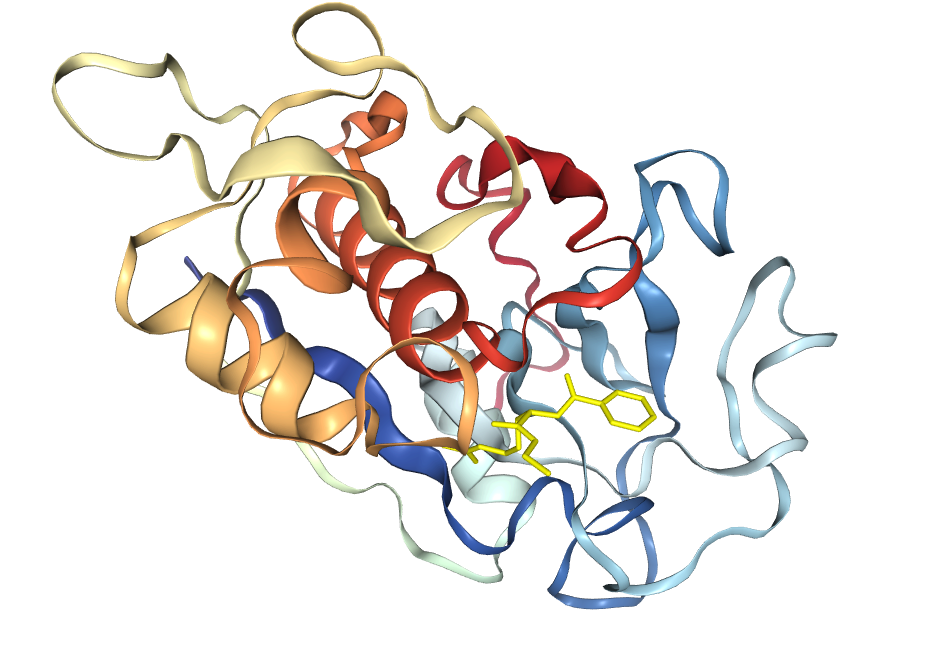
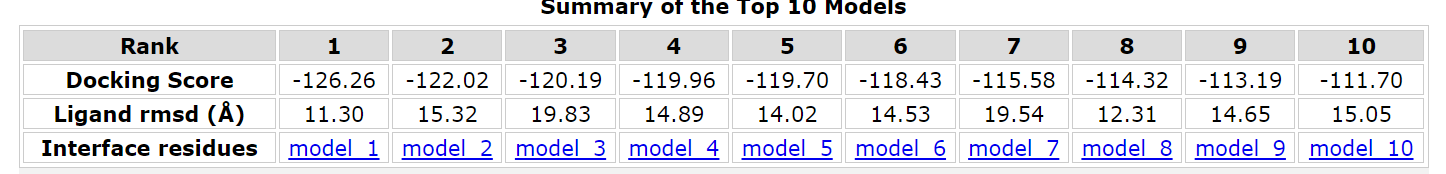
After literature review and network search, BAEE was finally determined as the reaction substrate of bromelain, and its docking and energy calculation were performed with bromelain and mutated variants. The calculations were done online by PDBePISA.
Finally, the binding energy of bromelain in wild-type was -125.09, while that in mutant was -126.26, which decreased. This also proves that the stem bromelain variant we developed is more easily bound to the substrate and its reactivity is enhanced.
(Figure 3a, b, c and d)
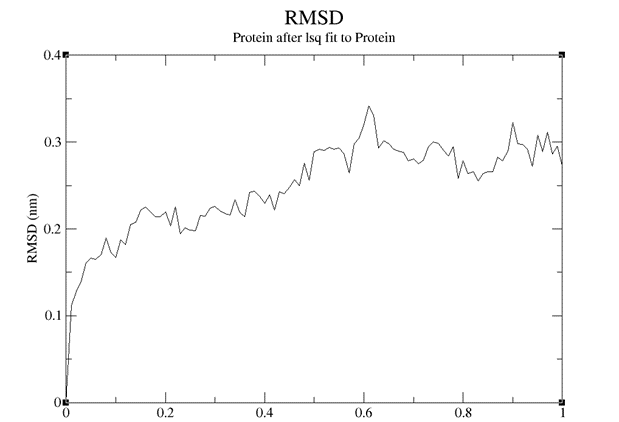
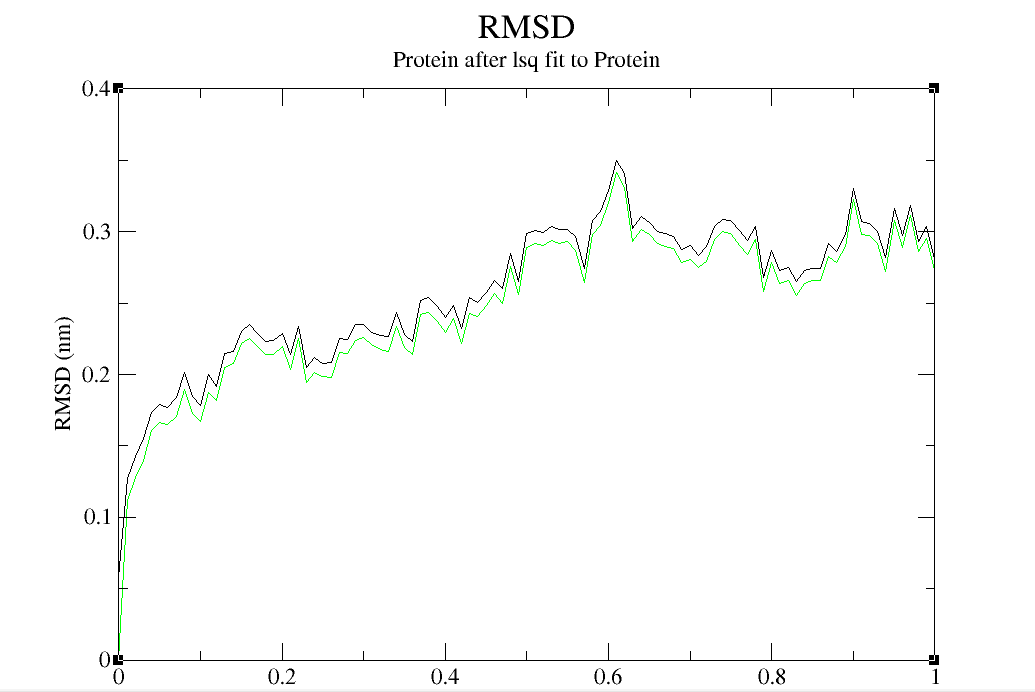
A molecular dynamics simulation was conducted to analyze the binding stability of Stem Bromelain(212aa) and BAEE complexes, where multiple descriptors were analyzed to understand the flexible and stable nature of the complexes. The system has been balanced in advance (the result of temperature and pressure balance is shown in below.(Figure4 a, b, c and d)
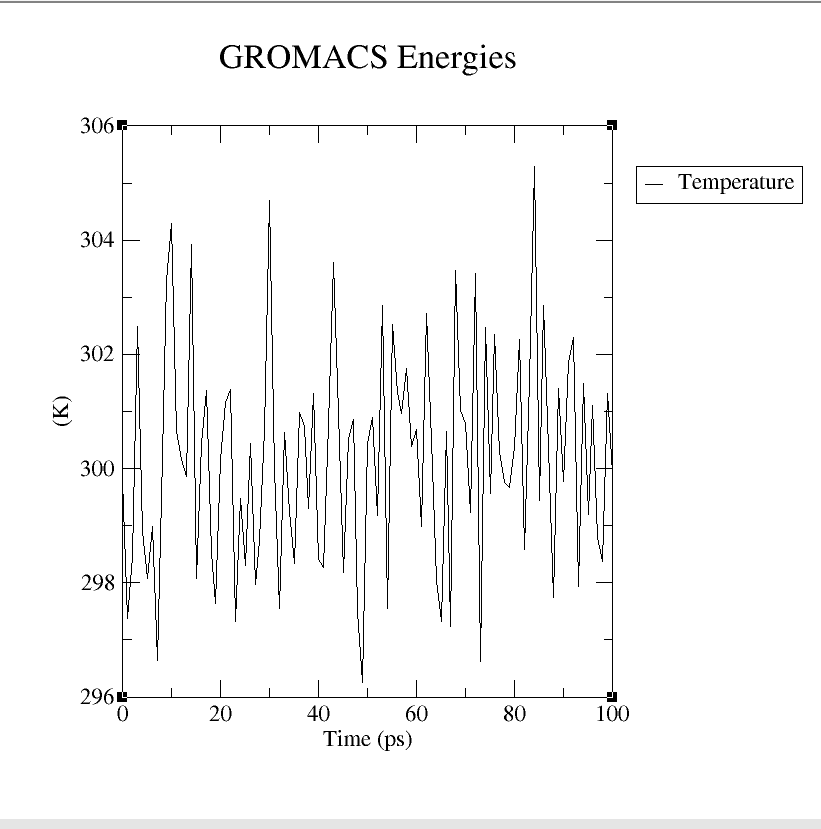
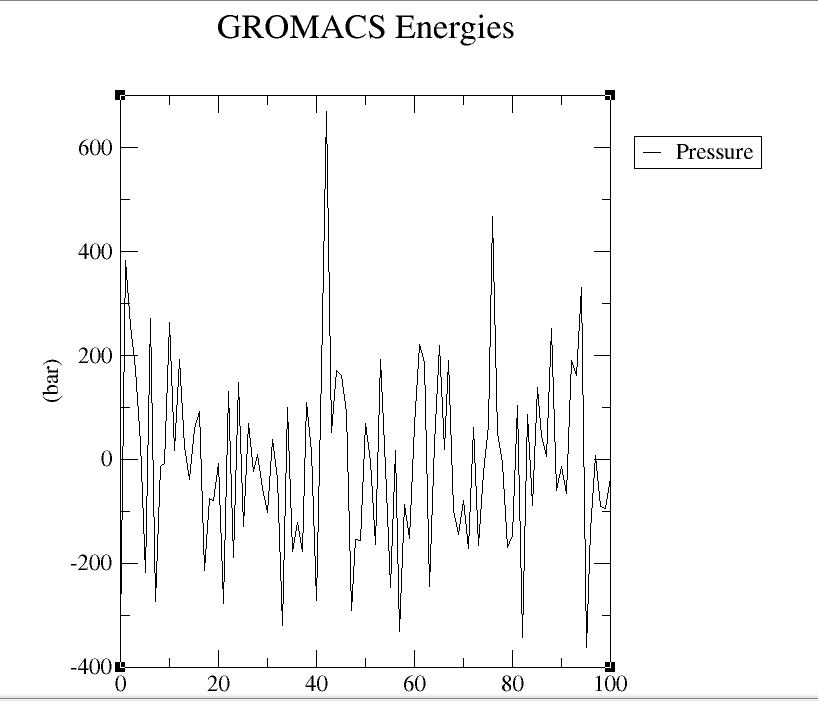
After the whole system was balanced, the molecular simulation started to run, which took 10h (1ns) in total.
RMSD and RMSF analysis were performed on the simulated results, and the results were shown in the figure below. It can be seen that Stem bromelain(212) has good reactivity with BAEE in neutral environment. The RMSD value was less than 0.4, and the RMSD value structure did not change much before and after simulation, indicating that the reaction between the complex was very stable. At the same time, the RMSF value changed greatly, which reflected that the atomic motion of Stem bromelain (212) was relatively free when it reacted with BAEE.